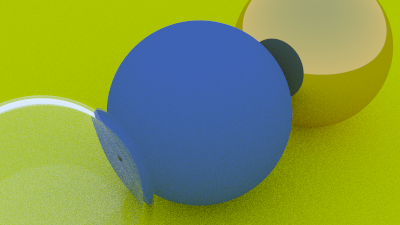
Positionable Camera
Cameras, like dielectrics, are hard to debug. So we’ll develop incrementally. First, let’s allow an adjustable field of view (fov). This is the angle you see through the portal. Since our image is not square, the fov is different horizontally and vertically. We’ll use vertical fov. We’ll also specify it in degrees and change to radians when creating the camera.
Camera Viewing Geometry
We first keep the rays coming from the origin and heading to the plane. We could make it the plane, or whatever, as long as we made a ratio to that distance. Here is our setup:
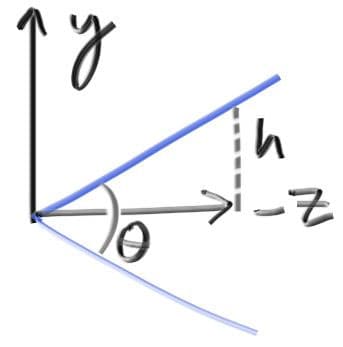
This implies . Our camera now becomes:
use crate::common;
use crate::ray::Ray;
use crate::vec3::{Point3, Vec3};
pub struct Camera {
origin: Point3,
lower_left_corner: Point3,
horizontal: Vec3,
vertical: Vec3,
}
impl Camera {
pub fn new(
vfov: f64, // Vertical field-of-view in degrees
aspect_ratio: f64,
) -> Camera {
let theta = common::degrees_to_radians(vfov);
let h = f64::tan(theta / 2.0);
let viewport_height = 2.0 * h;
let viewport_width = aspect_ratio * viewport_height;
let focal_length = 1.0;
let origin = Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
let horizontal = Vec3::new(viewport_width, 0.0, 0.0);
let vertical = Vec3::new(0.0, viewport_height, 0.0);
let lower_left_corner =
origin - horizontal / 2.0 - vertical / 2.0 - Vec3::new(0.0, 0.0, focal_length);
Camera {
origin,
lower_left_corner,
horizontal,
vertical,
}
}
pub fn get_ray(&self, u: f64, v: f64) -> Ray {
Ray::new(
self.origin,
self.lower_left_corner + u * self.horizontal + v * self.vertical - self.origin,
)
}
}When calling it with camera cam(90.0, aspect_ratio) and these spheres:
mod camera;
mod color;
mod common;
mod hittable;
mod hittable_list;
mod material;
mod ray;
mod sphere;
mod vec3;
use std::io;
use std::rc::Rc;
use camera::Camera;
use color::Color;
use hittable::{HitRecord, Hittable};
use hittable_list::HittableList;
use material::Lambertian;
use ray::Ray;
use sphere::Sphere;
use vec3::Point3;
fn ray_color(r: &Ray, world: &dyn Hittable, depth: i32) -> Color {
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered
if depth <= 0 {
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
let mut rec = HitRecord::new();
if world.hit(r, 0.001, common::INFINITY, &mut rec) {
let mut attenuation = Color::default();
let mut scattered = Ray::default();
if rec
.mat
.as_ref()
.unwrap()
.scatter(r, &rec, &mut attenuation, &mut scattered)
{
return attenuation * ray_color(&scattered, world, depth - 1);
}
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
let unit_direction = vec3::unit_vector(r.direction());
let t = 0.5 * (unit_direction.y() + 1.0);
(1.0 - t) * Color::new(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + t * Color::new(0.5, 0.7, 1.0)
}
fn main() {
// Image
const ASPECT_RATIO: f64 = 16.0 / 9.0;
const IMAGE_WIDTH: i32 = 400;
const IMAGE_HEIGHT: i32 = (IMAGE_WIDTH as f64 / ASPECT_RATIO) as i32;
const SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL: i32 = 100;
const MAX_DEPTH: i32 = 50;
// World
let r = f64::cos(common::PI / 4.0);
let mut world = HittableList::new();
let material_left = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)));
let material_right = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(-r, 0.0, -1.0),
r,
material_left,
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(r, 0.0, -1.0),
r,
material_right,
)));
// Camera
let cam = Camera::new(90.0, ASPECT_RATIO);
// Render
print!("P3\n{} {}\n255\n", IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT);
for j in (0..IMAGE_HEIGHT).rev() {
eprint!("\rScanlines remaining: {} ", j);
for i in 0..IMAGE_WIDTH {
let mut pixel_color = Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for _ in 0..SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL {
let u = (i as f64 + common::random_double()) / (IMAGE_WIDTH - 1) as f64;
let v = (j as f64 + common::random_double()) / (IMAGE_HEIGHT - 1) as f64;
let r = cam.get_ray(u, v);
pixel_color += ray_color(&r, &world, MAX_DEPTH);
}
color::write_color(&mut io::stdout(), pixel_color, SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL);
}
}
eprint!("\nDone.\n");
}gives:
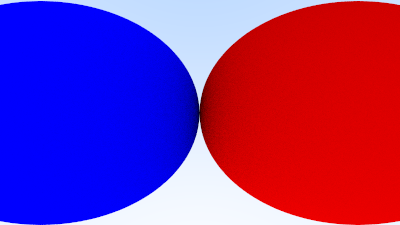
Positioning and Orienting the Camera
To get an arbitrary viewpoint, let’s first name the points we care about. We’ll call the position where we place the camera lookfrom, and the point we look at lookat. (Later, if you want, you could define a direction to look in instead of a point to look at.)
We also need a way to specify the roll, or sideways tilt, of the camera: the rotation around the lookat-lookfrom axis. Another way to think about it is that even if you keep lookfrom and lookat constant, you can still rotate your head around your nose. What we need is a way to specify an “up” vector for the camera. This up vector should lie in the plane orthogonal to the view direction.
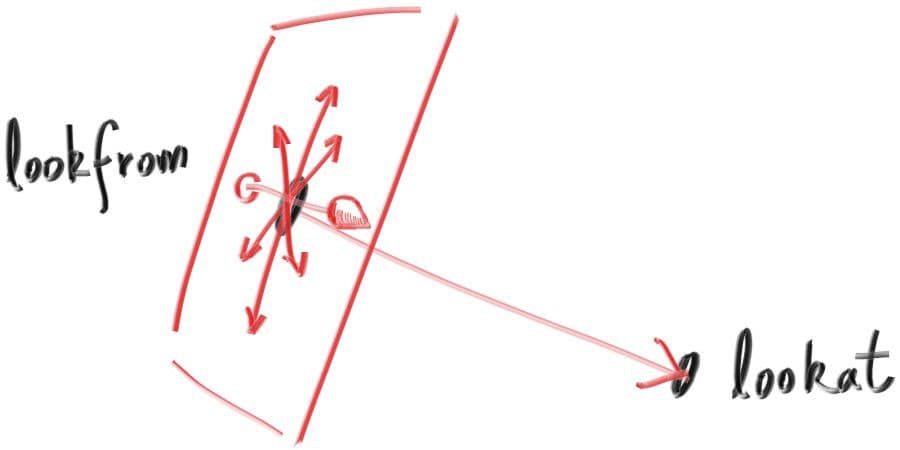
We can actually use any up vector we want, and simply project it onto this plane to get an up vector for the camera. We use the common convention of naming a “view up” (vup) vector. A couple of cross products, and we now have a complete orthonormal basis to describe our camera’s orientation.
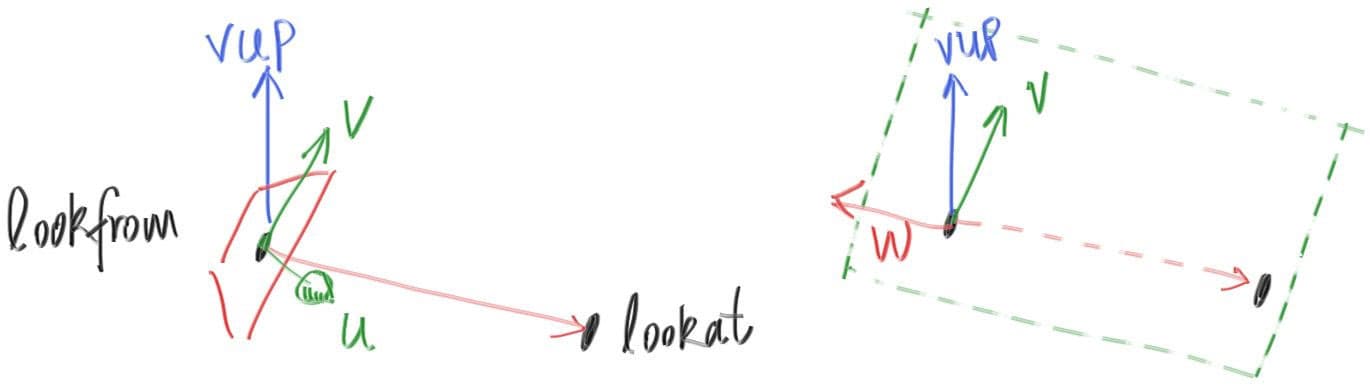
Remember that vup, v, and w are all in the same plane. Note that, like before when our fixed camera faced -Z, our arbitrary view camera faces -w. And keep in mind that we can — but we don’t have to — use world up to specify vup. This is convenient and will naturally keep your camera horizontally level until you decide to experiment with crazy camera angles.
use crate::common;
use crate::ray::Ray;
use crate::vec3::{self, Point3, Vec3};
pub struct Camera {
origin: Point3,
lower_left_corner: Point3,
horizontal: Vec3,
vertical: Vec3,
}
impl Camera {
pub fn new(
lookfrom: Point3,
lookat: Point3,
vup: Vec3,
vfov: f64, // Vertical field-of-view in degrees
aspect_ratio: f64,
) -> Camera {
let theta = common::degrees_to_radians(vfov);
let h = f64::tan(theta / 2.0);
let viewport_height = 2.0 * h;
let viewport_width = aspect_ratio * viewport_height;
let w = vec3::unit_vector(lookfrom - lookat);
let u = vec3::unit_vector(vec3::cross(vup, w));
let v = vec3::cross(w, u);
let origin = lookfrom;
let horizontal = viewport_width * u;
let vertical = viewport_height * v;
let lower_left_corner = origin - horizontal / 2.0 - vertical / 2.0 - w;
Camera {
origin,
lower_left_corner,
horizontal,
vertical,
}
}
pub fn get_ray(&self, s: f64, t: f64) -> Ray {
Ray::new(
self.origin,
self.lower_left_corner + s * self.horizontal + t * self.vertical - self.origin,
)
}
}We’ll change back to the prior scene, and use the new viewpoint:
mod camera;
mod color;
mod common;
mod hittable;
mod hittable_list;
mod material;
mod ray;
mod sphere;
mod vec3;
use std::io;
use std::rc::Rc;
use camera::Camera;
use color::Color;
use hittable::{HitRecord, Hittable};
use hittable_list::HittableList;
use material::{Dielectric, Lambertian, Metal};
use ray::Ray;
use sphere::Sphere;
use vec3::{Point3, Vec3};
fn ray_color(r: &Ray, world: &dyn Hittable, depth: i32) -> Color {
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered
if depth <= 0 {
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
let mut rec = HitRecord::new();
if world.hit(r, 0.001, common::INFINITY, &mut rec) {
let mut attenuation = Color::default();
let mut scattered = Ray::default();
if rec
.mat
.as_ref()
.unwrap()
.scatter(r, &rec, &mut attenuation, &mut scattered)
{
return attenuation * ray_color(&scattered, world, depth - 1);
}
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
let unit_direction = vec3::unit_vector(r.direction());
let t = 0.5 * (unit_direction.y() + 1.0);
(1.0 - t) * Color::new(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + t * Color::new(0.5, 0.7, 1.0)
}
fn main() {
// Image
const ASPECT_RATIO: f64 = 16.0 / 9.0;
const IMAGE_WIDTH: i32 = 400;
const IMAGE_HEIGHT: i32 = (IMAGE_WIDTH as f64 / ASPECT_RATIO) as i32;
const SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL: i32 = 100;
const MAX_DEPTH: i32 = 50;
// World
let mut world = HittableList::new();
let material_ground = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(0.8, 0.8, 0.0)));
let material_center = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(0.1, 0.2, 0.5)));
let material_left = Rc::new(Dielectric::new(1.5));
let material_right = Rc::new(Metal::new(Color::new(0.8, 0.6, 0.2), 0.0));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(0.0, -100.5, -1.0),
100.0,
material_ground,
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, -1.0),
0.5,
material_center,
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(-1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
0.5,
material_left.clone(),
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(-1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
-0.45,
material_left,
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
0.5,
material_right,
)));
// Camera
let cam = Camera::new(
Point3::new(-2.0, 2.0, 1.0),
Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, -1.0),
Vec3::new(0.0, 1.0, 0.0),
90.0,
ASPECT_RATIO,
);
// Render
print!("P3\n{} {}\n255\n", IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT);
for j in (0..IMAGE_HEIGHT).rev() {
eprint!("\rScanlines remaining: {} ", j);
for i in 0..IMAGE_WIDTH {
let mut pixel_color = Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for _ in 0..SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL {
let u = (i as f64 + common::random_double()) / (IMAGE_WIDTH - 1) as f64;
let v = (j as f64 + common::random_double()) / (IMAGE_HEIGHT - 1) as f64;
let r = cam.get_ray(u, v);
pixel_color += ray_color(&r, &world, MAX_DEPTH);
}
color::write_color(&mut io::stdout(), pixel_color, SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL);
}
}
eprint!("\nDone.\n");
}to get:
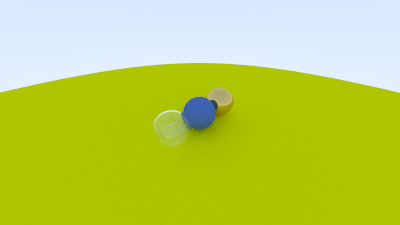
And we can change field of view:
mod camera;
mod color;
mod common;
mod hittable;
mod hittable_list;
mod material;
mod ray;
mod sphere;
mod vec3;
use std::io;
use std::rc::Rc;
use camera::Camera;
use color::Color;
use hittable::{HitRecord, Hittable};
use hittable_list::HittableList;
use material::{Dielectric, Lambertian, Metal};
use ray::Ray;
use sphere::Sphere;
use vec3::{Point3, Vec3};
fn ray_color(r: &Ray, world: &dyn Hittable, depth: i32) -> Color {
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered
if depth <= 0 {
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
let mut rec = HitRecord::new();
if world.hit(r, 0.001, common::INFINITY, &mut rec) {
let mut attenuation = Color::default();
let mut scattered = Ray::default();
if rec
.mat
.as_ref()
.unwrap()
.scatter(r, &rec, &mut attenuation, &mut scattered)
{
return attenuation * ray_color(&scattered, world, depth - 1);
}
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
let unit_direction = vec3::unit_vector(r.direction());
let t = 0.5 * (unit_direction.y() + 1.0);
(1.0 - t) * Color::new(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + t * Color::new(0.5, 0.7, 1.0)
}
fn main() {
// Image
const ASPECT_RATIO: f64 = 16.0 / 9.0;
const IMAGE_WIDTH: i32 = 400;
const IMAGE_HEIGHT: i32 = (IMAGE_WIDTH as f64 / ASPECT_RATIO) as i32;
const SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL: i32 = 100;
const MAX_DEPTH: i32 = 50;
// World
let mut world = HittableList::new();
let material_ground = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(0.8, 0.8, 0.0)));
let material_center = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(0.1, 0.2, 0.5)));
let material_left = Rc::new(Dielectric::new(1.5));
let material_right = Rc::new(Metal::new(Color::new(0.8, 0.6, 0.2), 0.0));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(0.0, -100.5, -1.0),
100.0,
material_ground,
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, -1.0),
0.5,
material_center,
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(-1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
0.5,
material_left.clone(),
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(-1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
-0.45,
material_left,
)));
world.add(Box::new(Sphere::new(
Point3::new(1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
0.5,
material_right,
)));
// Camera
let cam = Camera::new(
Point3::new(-2.0, 2.0, 1.0),
Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, -1.0),
Vec3::new(0.0, 1.0, 0.0),
20.0,
ASPECT_RATIO,
);
// Render
print!("P3\n{} {}\n255\n", IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT);
for j in (0..IMAGE_HEIGHT).rev() {
eprint!("\rScanlines remaining: {} ", j);
for i in 0..IMAGE_WIDTH {
let mut pixel_color = Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for _ in 0..SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL {
let u = (i as f64 + common::random_double()) / (IMAGE_WIDTH - 1) as f64;
let v = (j as f64 + common::random_double()) / (IMAGE_HEIGHT - 1) as f64;
let r = cam.get_ray(u, v);
pixel_color += ray_color(&r, &world, MAX_DEPTH);
}
color::write_color(&mut io::stdout(), pixel_color, SAMPLES_PER_PIXEL);
}
}
eprint!("\nDone.\n");
}to get: